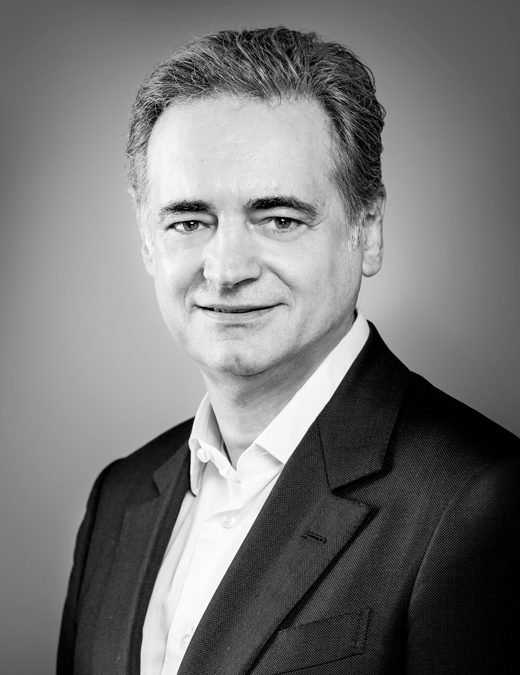
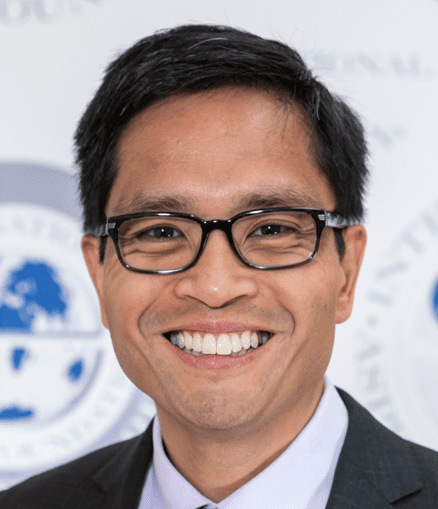
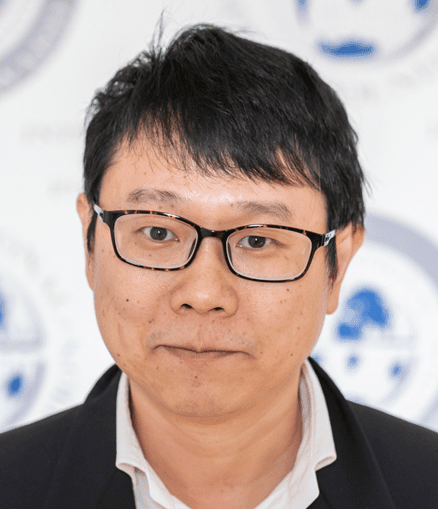
Dr Manuel Mendoza wins the Emerging Aspirin Investigator Science Award

The International Aspirin Foundation presents Dr Manel Mendoza with the prestigious Emerging Aspirin Investigator Science Award for his ground-breaking work defining the optimal duration of aspirin treatment for the prevention of preeclampsia. The International Aspirin Foundation (IAF)’s Science Award for the Emerging Aspirin Investigator recognises scientists in the early stages of their research career. The […]
Aspirin Tributes Booklet

Aspirin Tributes Read all Aspirin Tributes in one convenient brochure with contributions from Dr Luis A Garcia Rodriguez, Prof Gemma Vilahur, Prof Bianca Rocca, Prof Ruth Langley, Prof Junbo Ge and Dr Elisa Llurba who each share their aspirin hero, why they are such big fans of aspirin, their past and current aspirin studies and […]
EuroCVP 2023 – The annual meeting on advances in cardiovascular pharmacotherapy

EuroCVP 2023 – The annual meeting on advances in cardiovascular pharmacotherapy 2 November – 4 November 2023 Seminar (Florence, IT) Organiser: WG on Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Topic: Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy EuroCVP 2023 – Advances in Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy is the annual meeting of the ESC Working Group on Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy (ESC WG CVP). This event offers an outstanding scientific programme […]
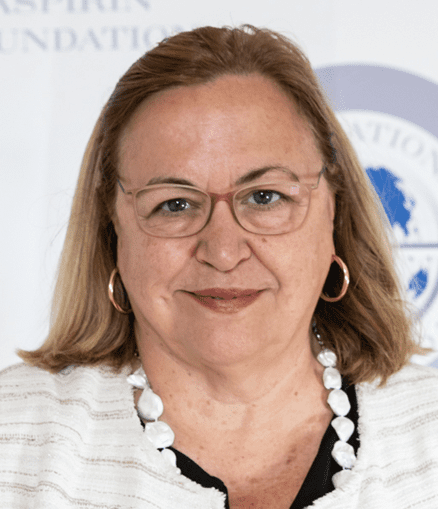
Aspirin Tributes : Dr Elisa Llurba

Aspirin Tributes Dr Elisa Llurba, a maternal and foetal medicine specialist, discusses the exploration of aspirin including giving it to women undergoing IVF prior to implantation and to women who have suffered preeclampsia to see if it benefits their long-term cardiovascular health. Read the full conversation here.
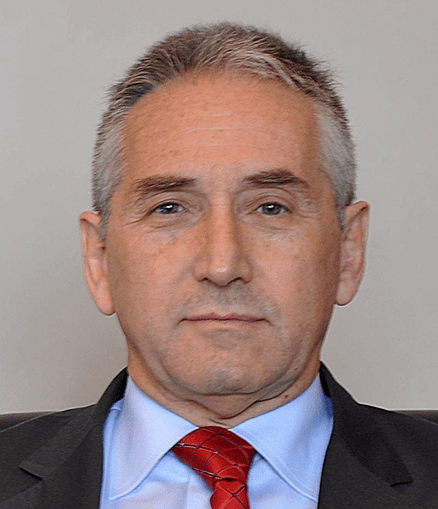
Dr Andrew Chan appointed as Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board of the International Aspirin Foundation

The International Aspirin Foundation has today announced that Dr Andrew Chan will become Chair of its Scientific Advisory Board. Dr Chan succeeds Professor Carlo Patrono who will retire from the role, having led the Board since 2017.Dr Chan is Chief of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit and Vice Chair of the Division of Gastroenterology […]
Aspirin Tributes : Professor Ruth Langley
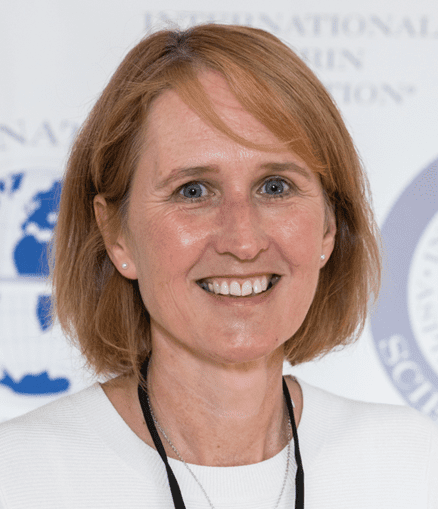

Aspirin Tributes Professor Ruth Langley has a particular interest in drug repurposing and is chief investigator of the Add-Aspirin trial. In this edition, Ruth discusses her inspiration and interest in aspirin, the role aspirin plays in cancer, as well as secondary and primary prevention. Read the full conversation here.
Aspirin Tributes : Professor Bianca Rocca

Aspirin Tributes Professor Bianca Rocca motivated by platelets and aspirin throughout her career. Bianca gives her views on the limitations of the ARRIVE & ASPREE trials; and discusses the future of personalised medicine and precision dosing. Read the full conversation here.
Aspirin Tributes : Professor Gemma Vilahur
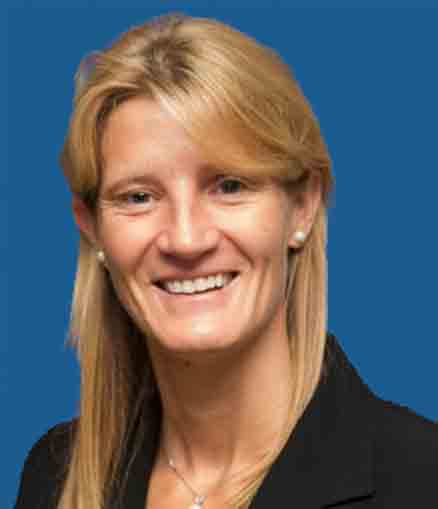

Aspirin Tributes Professor Gemma Vilahur discusses her aspirin heroine, the role aspirin plays in the primary prevention of CVD, why aspirin is beneficial in patients with DM and the studies she has undertaken in that area, as well as why she is such a big aspirin fan. Read the full conversation here.
Aspirin Tributes : Dr Luis A. Garcia Rodriguez

Aspirin Tributes Dr Luis A Garcia Rodriguez explains why he is such a big aspirin fan To my mind the low cost of aspirin together with its favourable risk/ benefit profile helps to deliver a bigger bang for the buck than almost any other drug. Because aspirin is off patent taking it every day costs […]
The International Aspirin Foundation presents Dr Tracey Simon with the prestigious Emerging Aspirin Investigator Science Award for her seminal work linking aspirin with hepatocellular cancer prevention.
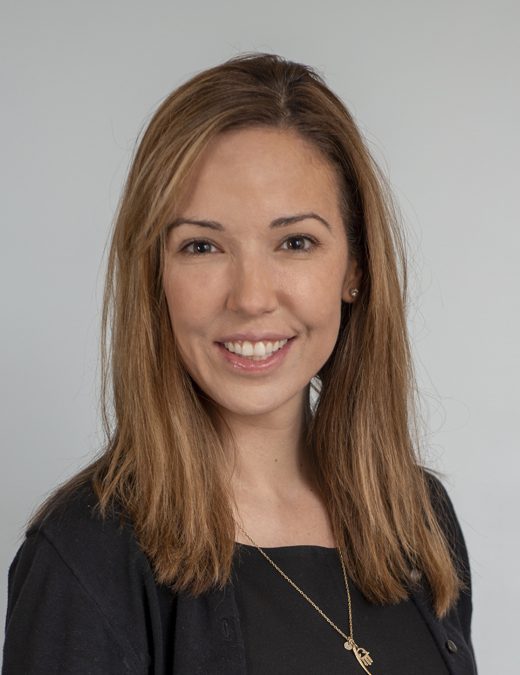

The International Aspirin Foundation presents Dr Tracey Simon with the prestigious Emerging Aspirin Investigator Science Award for her seminal work linking aspirin with hepatocellular cancer prevention. The International Aspirin Foundation (IAF)’s Science Award for the Emerging Aspirin Investigator recognises junior scientists in the early stages of their research career. The award aims to acknowledge and […]